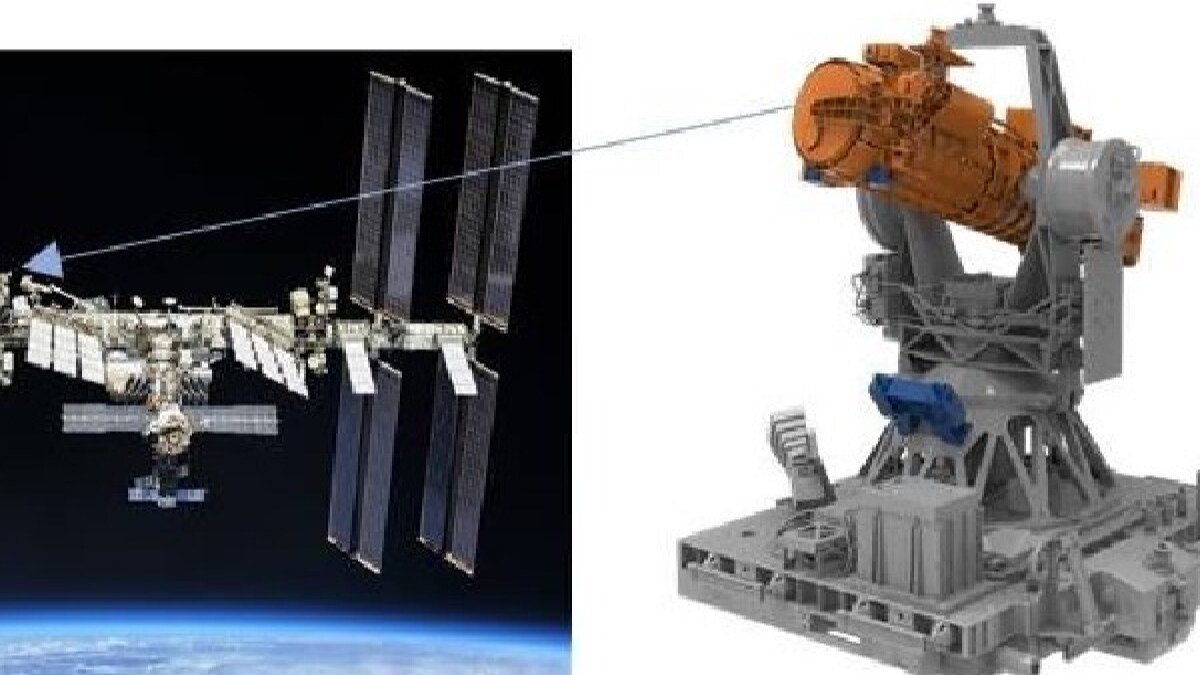

South Korea’s area company introduced plans on Friday to launch a photo voltaic coronagraph to the Worldwide House Station (ISS) in a collaborative mission with NASA. Developed as a part of the Coronal Diagnostic Experiment (CODEX), this instrument is about to look at and collect information on the Solar’s corona and the photo voltaic wind in addition to the stream of charged particles that flows from the Solar’s outer ambiance. The CODEX system is scheduled to be launched aboard SpaceX’s Falcon 9 from Florida’s Kennedy House Middle on Monday, as reported by Yonhap Information Company.
Bilateral Venture to Study Photo voltaic Environment
The CODEX mission represents an important collaboration between the Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KASA) and NASA, with CODEX marking a pioneering achievement because the world’s first coronagraph outfitted to measure temperature, velocity, and density inside the photo voltaic wind. As soon as aboard the ISS, CODEX might be mounted on the station’s specific logistics service, permitting for approx 55 minutes of photo voltaic statement in every 90-minute orbit round Earth. This information is anticipated to reinforce researchers’ understanding of the photo voltaic wind, doubtlessly aiding in area climate forecasting efforts.
South Korea’s Expanded Cooperation with NASA
Alongside the CODEX mission, South Korea and america have broadened their partnership in area exploration. KASA and NASA signed an announcement of cooperation, specializing in analysis initiatives together with the Artemis lunar exploration programme. KASA’s involvement with the Artemis mission consists of research on sustainable lunar exploration and developments in Mars mission preparations. With this settlement, South Korea has grow to be the fifth nation to formally collaborate with NASA on such initiatives.
Pioneering Research and Technological Developments
Below the framework of this settlement, South Korea and the US will work collectively on a wide range of feasibility research associated to lunar landers, in addition to developments in communication, navigation, and astronaut assist techniques. As well as, collaborative efforts will span lunar floor science, autonomous energy, robotic techniques, and cis-lunar area operations—the realm between Earth and the Moon.






